
INDIANA – In all weather conditions, the body works hard to maintain a normal temperature of 98.6 degrees. When temperatures are drastic, whether it’s a scorching summer day, it can be even more difficult for your body to maintain this ideal temperature.
A rapid rise in heat due to exposure to hotter-than-average conditions compromises the body’s ability to regulate temperature and can result in a cascade of illnesses including heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and hyperthermia.
Even at rest, the human body produces a lot of heat energy. When it’s cool, your body will expel this heat through radiation. The heat simply radiates from the body to the surrounding air.
When it’s hot, your body sweats to keep you cool. Perspiration comes to the surface of your skin. As it evaporates, you begin to feel cooler. When it’s humid outside, it’s harder for the perspiration on the surface of your skin to evaporate, because the air is already saturated with moisture. That’s why people often say it’s not the heat but the humidity that makes it unbearable to be outside on a hot day — though both play a role in your body’s overheating.
Extreme Heat Is Dangerous — and Sometimes Deadly
In a typical year, about 618 Americans die from extreme heat, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Seniors, young children, and people with mental illness and chronic conditions like heart disease are at the highest risk, the CDC says, and athletes, outdoor workers, and people of color are particularly vulnerable.
Men Sweat More Than Women
While women have more sweat glands than men, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine, men’s sweat glands are more active, leading them to sweat more than women. The more you sweat, the more easily you can become dehydrated which can lead to other health issues.
You Have Up to 4 Million Sweat Glands in Your Body
That’s according to the International Hyperhidrosis Society. There are two types of sweat glands: eccrine and apocrine. Both produce fluids. The area of the brain known as the hypothalamus controls your body temperature by regulating sweat output and blood flow to the skin. The odor associated with sweat comes from the apocrine glands found in the armpits and genital region; the sweat from these glands produces a smell when it comes in contact with bacteria on the skin.
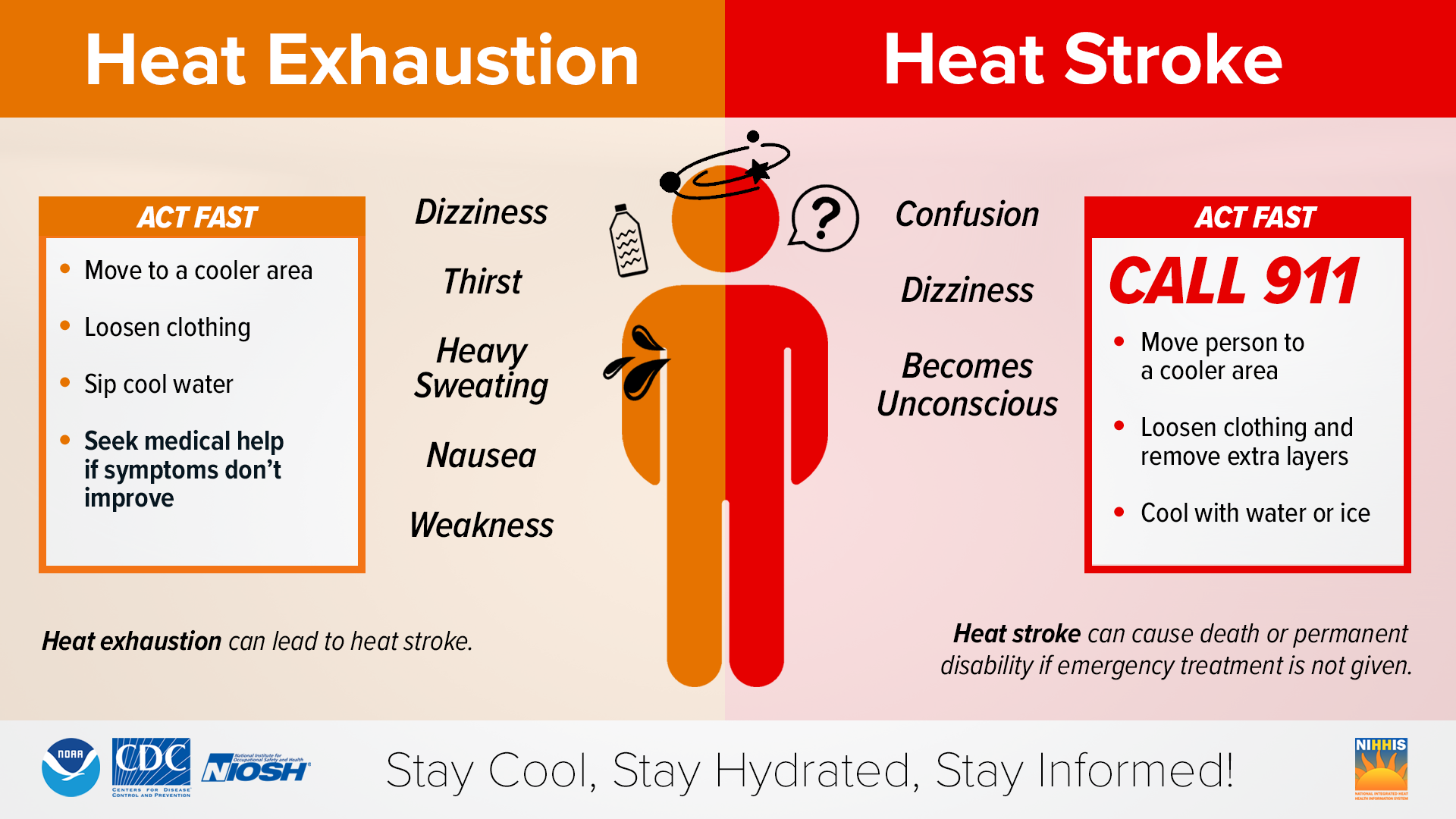
Heat Exhaustion Occurs When Your Body Overheats
Warning signs of heat exhaustion include dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, heavy sweating, and headache, according to the CDC. To treat heat exhaustion, move to a cool location, drink lots of water, soak in a cool bath or use cool compresses.
Being Overheated Can Lead to life-threatening Heatstroke
Heatstroke can occur when your body temperature reaches at least 104 degrees; at this point, your body loses the ability to regulate temperature on its own, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP). According to the CDC, signs of heatstroke include muscle cramping, a fast heartbeat, vomiting, flushed skin, headache, mental confusion, and seizures. Call 911 immediately. Someone experiencing heat stroke should be moved to a cooler place and given a bath of cool water or compresses.
You Can Protect Yourself From Heatstroke by Staying Hydrated
Drink water before you are thirsty. In extreme heat, it’s best to avoid caffeine and alcohol, the American Academy of Family Physicians advises. Wear loose clothing that allows the air to circulate around you as you exercise, and avoid exercising outdoors during the hottest part of the day, which is often from 11 a.m. to 6 p.m. Instead, schedule your workout as close to sunrise or sunset as possible.
Infants and Small Children, Elderly, and those with Diabetes are at High Risk of Heat-Related Illnesses
Infants and small children can’t control their environment (if they’re left in a room or vehicle that is hot, for example); they have a high metabolic rate, which means their bodies are producing heat constantly; and they aren’t able to perspire as much as adults. Never leave a child in a parked car, even with the windows open.
That includes those who are morbidly obese, the elderly, and people who are immobile. People with diabetes can be heat sensitive, too. If you have diabetes and you become dehydrated from the heat, it can affect your blood sugar levels. Be sure to keep insulin and other diabetes medications out of the heat, as hot temperatures can ruin them. People with multiple sclerosis may find that their symptoms worsen when they’re hot. When heat raises a person’s body temperature, it becomes harder for the central nervous system to work properly.
Some Medications Can Put You at Increased Risk of Heatstroke
These include some kinds of allergy medicines and antihistamines, blood pressure and heart medications, diuretics, laxatives, antidepressants, and seizure medications, according to the AAFP. Talk to your doctor about what precautions are important if you’re taking any of these.



